Protection and responsible use
of natural resources
In order to contribute to preserving the global environment and creating sustainable societies, the JCU Group is committed to make efficient use of energy and resources.
Use of Renewable Energy

The JCU Group is driving forward with the use of renewable energy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Among our domestic offices, we have installed solar power generation equipment to reduce CO2 emissions at our Niigata Plant in Niigata and R&D Center in Kanagawa, both of which particularly consume large amounts of electricity. We are working to use renewable energy at our overseas business locations, and have installed solar power facilities at our plant in Hubei, China that are capable of producing about 40% of the plant’s maximum electricity consumption.
In addition, at our Kumamoto Facility, which will house a production plant and research lab, is scheduled for completion in December 2025. we plan to install high-capacity solar power generation equipment and introduce a variety of cutting-edge energy-saving equipment, making it an exceptionally environmentally friendly facility.
JCU will continue to implement a wide array of initiatives to realize a decarbonized society.
Effect of introducing solar power generation facilities
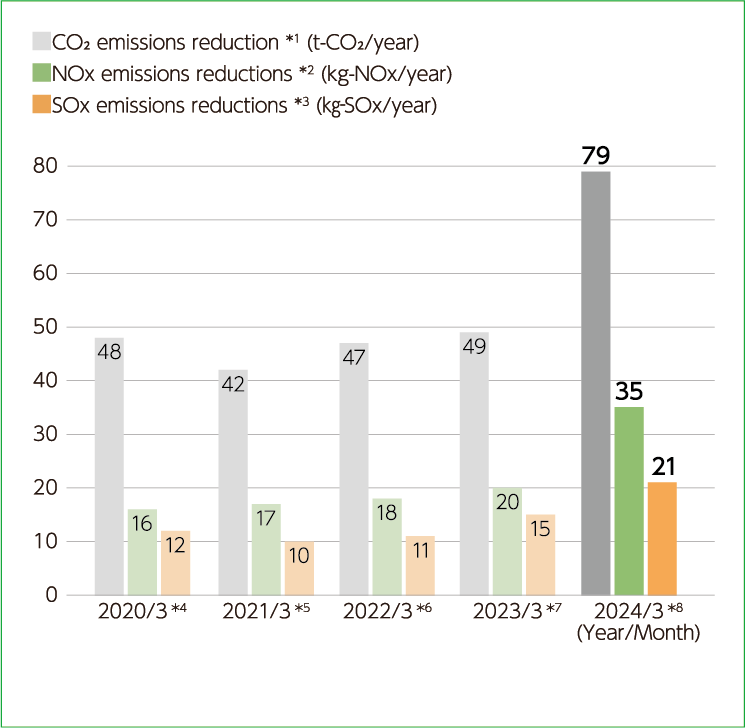
- Actual carbon dioxide (CO₂) emission factors from valuespublished by the Tohoku Electric Power Company are used.
- Nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission intensity from valuespublished by the Tohoku Electric Power Company is used.
- Sulfur oxide (SOx) emission intensity from values published by the Tohoku Electric Power Company are used.
- actors of performance in the FY ending March 2019 are used.
- actors of performance in the FY ending March 2020 are used.
- actors of performance in the FY ending March 2021 are used.
- actors of performance in the FY ending March 2022 are used.
- actors of performance in the FY ending March 2023 are used.
Changes in electricity consumption and in-house power generation at the production division (Installed solar power capacity: 100kW)
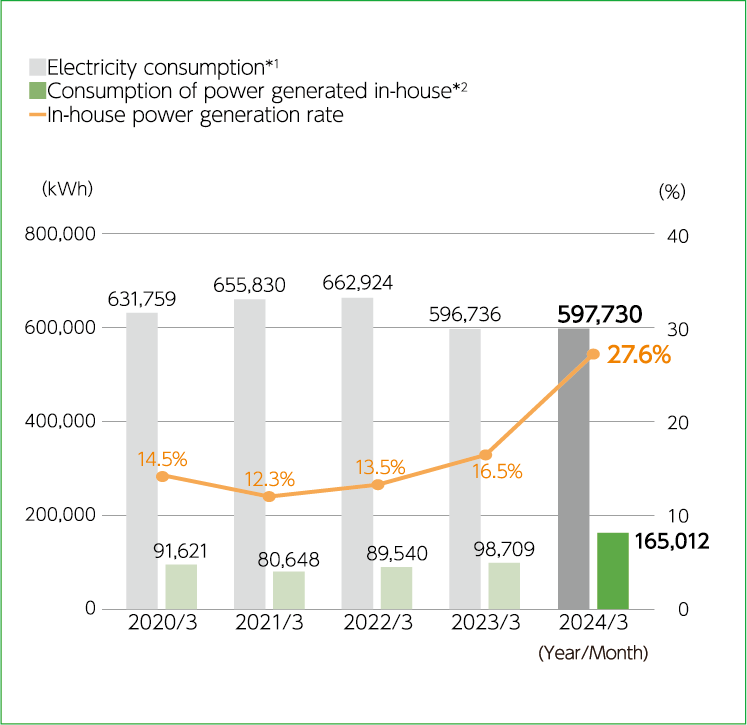
- Electricity consumption = Electricity purchased + Electricity generated - Electricity sold
- Excluding electricity sold
Total CO₂ emissions at offices in Japan by fiscal year
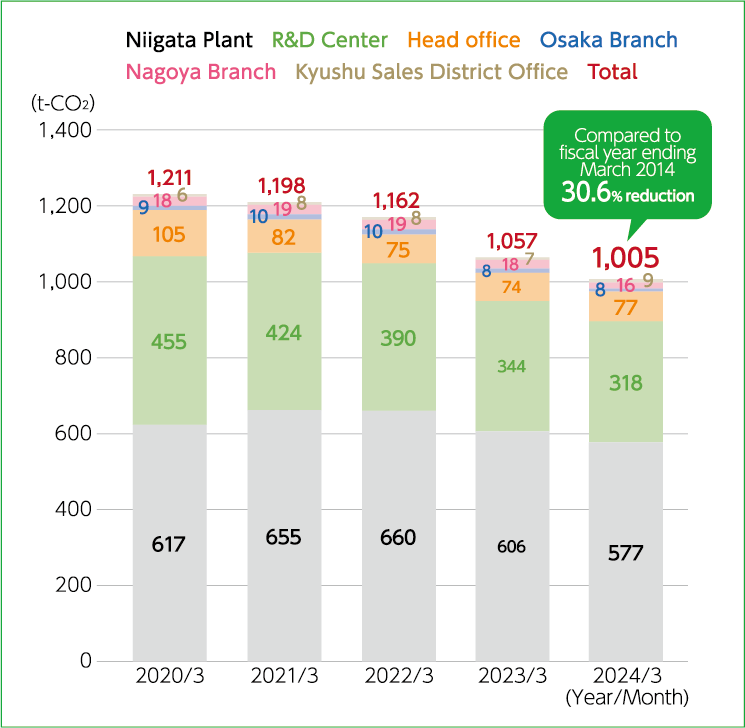
- This is calculated for electricity and gas at each office.
- The calculations use factors from organizations including Tohoku Electric Power Company, Kansai Electric Power Company, Chubu Electric Power Company, Kyushu Electric Power Company, Joetsu City Gas and Water Bureau, Toho Gas Company,Tokyo Gas Company, and the Liquefied Petroleum Gas Association.
Carbon Offsetting Initiatives
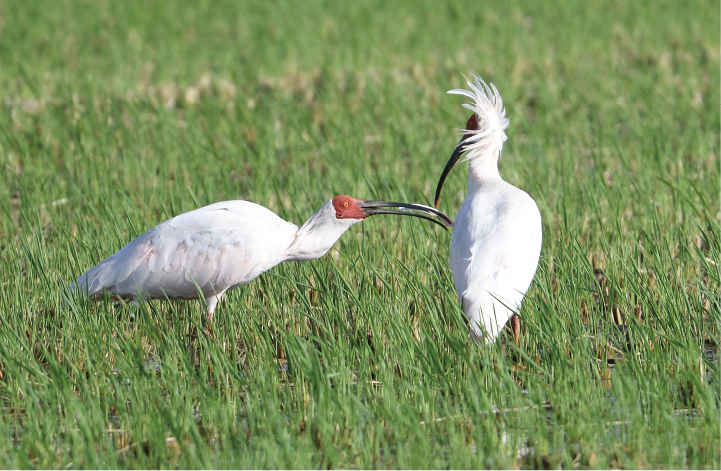
From its location in Joetsu City, Niigata Prefecture, JCU's Niigata Plant supplies products destined for markets around the world. JCU is an advocate of the “Toki-no-Mori (Crested Ibis Forest) Project” which is run by the Prefecture of Niigata within Sado City limits, and is also an ongoing collaborator in carbon offsetting initiatives.
The aim of the Toki-no-Mori Project is to drive global warming countermeasures forward by securing the CO₂ absorption capacity of trees, promote forest improvements, and revitalize forestry. The Project also aims to contribute to improving habitats for ibises that have been released into the wild and conserving the forest’s rich ecosystem.
In a forest within Sado City limits in Niigata, we see trees that have been culled with their lower branches pruned. Culling and pruning trees ensures that the forest gets enough light intensity, which in turn improves its CO₂ absorption efficiency. In addition, these procedures have the effect of suppressing pest insect outbreaks and promoting tree growth. These human interventions are a driver of our global warming countermeasures.
Currently, although their numbers are still small, we are able to observe ibises in the wild within Sado City limits. The ibises are gradually returning to their wild habitats thanks not only to the Toki-no-Mori Project but also to various activities by local residents for improving the environment around their habitats.


Initiatives to achieve “Zero CO₂ Emissions”
As a measure to counter global warming, JCU makes every effort to identify and reduce carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions.
An aggregate survey of CO₂ emissions from using electricity and gas at our domestic business locations shows that we have succeeded in reducing emissions in the FY ending March 2024 by 30.6% from the FY ending March 2014.
The Niigata Plant and R&D Center collectively account for about 90% of our total domestic CO₂ emissions.
The Niigata Plant has been actively introducing renewable sources of energy, installing solar power generation facilities ahead of other sites, and making additions to these in 2022. As a result, the percentage of on-site solar-generated power grew by 11.1% from the previous year to 27.6%.
In addition, environmentally friendly activities are also constantly ongoing at the R&D Center, including the installation of a solar power generation system, energy-efficient air conditioning equipment, and LED lighting.
In our Medium-Term Management Plan, the JCU Group has set a goal of reducing CO₂ emissions at our Niigata Plant to net zero by the FY ending March 2031, and of reducing total emissions from all domestic business locations to net zero by the FY ending March 2051 based on emissions in the FY ending March 2014. The JCU Group will continue to make efforts to achieve its goals and contribute to society through environmentally conscious corporate activities.
Carbon offsetting
Although the reduction of CO₂ and greenhouse gas emissions is very important in countering global warming, CO₂ emissions remain an inevitable part of our daily lives and corporate activities.
Carbon offsetting refers to methods for making up for (offsetting) all or part of the CO₂ emissions that occur despite our best emissions reduction efforts by funding forest improvement and other greenhouse gas reduction projects.
Understanding Water Usage
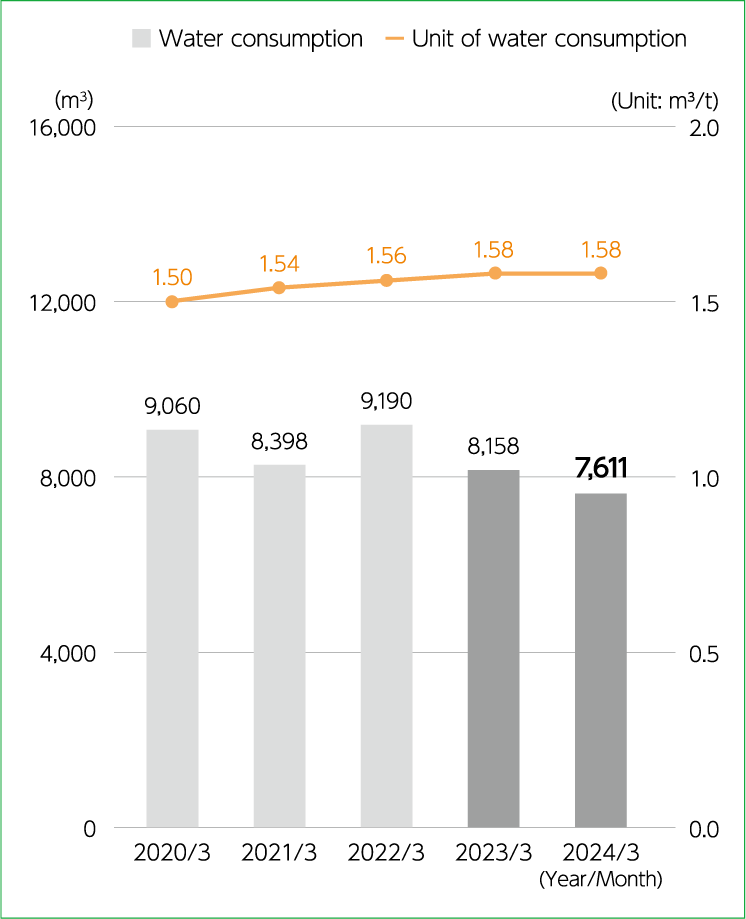
Because JCU uses large amounts of water resources for R&D and at our production sites, we make every effort to understand and reduce water consumption at all of our domestic business locations.
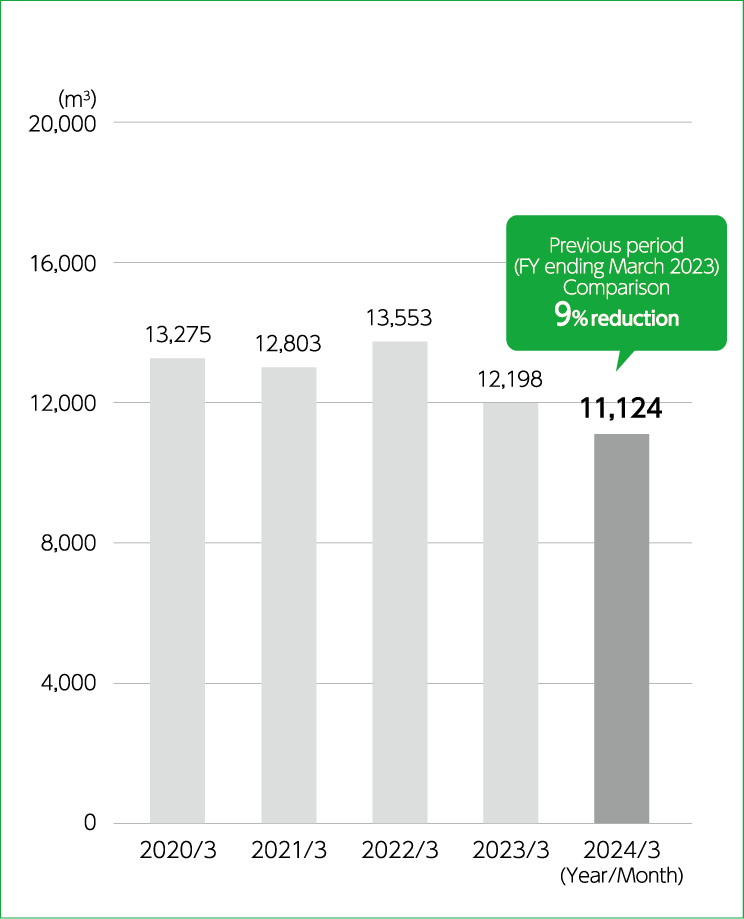
Domestic business locations took in a total of 11,124 m3 of water in the FY ending March 2024, which was a roughly 9% decrease from the previous fiscal year. Meanwhile, the unit of water consumption per production volume at the Niigata Plant remained unchanged from the previous fiscal year at 1.58 m3/t.
We believe this reduction in water withdrawal can be attributed mainly to the drop in production volume at the Niigata Plant compared to the previous fiscal year.
Water is one of the more important raw materials for manufacturing our products. Solving water resource issues is included as one of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). At our Kumamoto Facility, which is scheduled for completion in December 2025, we are planning to recycle water and eliminate water discharges at its factory and research buildings.
Annual water consumption
at domestic business
locations
Unit of water consumption
per production volume
at the Niigata Plant
Unit of water consumption
per number of employees
at the R&D Center

Proper Treatment of Wastewater
The JCU Group pays special attention to ensure that wastewater released from its development and manufacturing sites does not adversely affect the surrounding environment.
At the R&D Center, a portion of the wastewater generated during research is treated by neutralization and sedimentation using equipment in the facility. In addition, water discharged at all business sites are managed using analytical instruments to ensure that it meets environmental standards.
Furthermore, all sites concentrate and reduce the volumes of effluent that they are unable to treat in their own facilities before they are properly disposed of as industrial waste.
Proper Management of Chemical Substances
The JCU Group properly manages environmental chemicals to reduce our impact on the environmental.
At the R&D Center, we take measures to keep solution containers from tipping over, and also install embankments, pits, and gutters in our experimental facilities to prevent liquid leakage to the outside. At the Niigata Plant, we take measures to prevent leakage by installing oil embankments, pits and gutters for our outdoor tanks.
In addition, we always have response kits ready to use in the event of a leak, and we use these in our education and training programs to prepare for emergencies.

Raw Materials Recycling
The JCU Group is working to reduce the resources it uses through recycling and other initiatives. The R&D Center collects plating solutions and processed samples containing precious metals used in research and development, and recycles them to make effective use of resources. In addition, the Niigata Plant collects and recycles waste and cleaning water generated during product manufacturing to make effective use of resources.
Waste Reduction
The JCU Group makes every effort to make effective use of resources to reduce waste.
We reuse our one-ton containers for transporting specific products; that is, they are used on their way to and from our customers and business partners.
Also, empty poly containers that are no longer needed at the Niigata Plant are collected and recycled as a resource. After they are cleaned, these poly containers are melted down and reused in a variety of plastic products. In addition, metals, glass, and other waste materials are recycled as resources by waste disposal contractors.
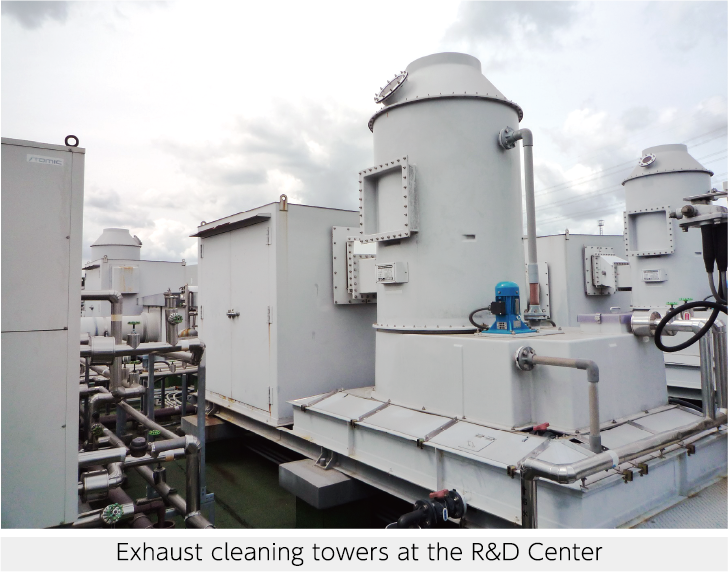
Purification of Atmospheric Emissions
At the JCU Group, we perform purification processes on gases that we discharge into the atmosphere from our business locations so that they do not affect the surrounding environment. We also make every effort to preserve the environment by conducting environmental measurements on a regular basis.
Our R&D Center and Niigata Plant are equipped with exhaust cleaning towers to prevent the release of hazardous substances contained in the discharged gas. We regularly commission specialized third-party agencies to analyze and verify that gas purification is being performed without any problems.
The Niigata Plant also regularly commissions specialized third-party agencies to analyze and examine the boilers and hot-and-chilled-water generators used at the site for particulate matter and nitrogen oxides to ensure that there are no problems.





